Outpatient Documentation & Coding Issues, September 2023
Presented below is an analysis of new and ongoing initiatives under the Office of the Inspector General (OIG) Work Plan [1] and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) approved Recovery Audit Contractor (RAC) reviews [2] as of July 2023. The focus is on outpatient initiatives related to HIM coding and documentation requirements and is not intended to review each and every active work plan item. For each relevant initiative, a summary of the OIG or RAC compliance concern, the month and year published and added to the plan, and related coding and documentation requirements is included below. More importantly, for each outpatient initiative presented, UASI has included specific suggested compliance activities to assist our clients with their ongoing compliance efforts.
The information below includes an analysis of the following active outpatient topics:
- Nationwide Audits of Medicare Part C High-Risk Diagnosis Codes (OIG)
- Minimally-Invasive Surgical (MIS) Fusion of the Sacroiliac Joint (RAC)
- Transurethral Waterjet Ablation of the Prostate for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) (RAC)
- Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation for Obstructive Sleep Apnea (RAC)
Nationwide Audits of Medicare Part C High-Risk Diagnosis Codes, June 2023
Medicare Advantage (MA) organizations receive risk-adjusted reimbursement based on the health status of each enrollee. All MA organizations submit risk-adjustment data to CMS according to defined regulations. Mis-coded diagnoses can result in incorrect payments back to MA organizations. These audits will focus on identified high risk diagnoses being mis-coded and resulting in increased risk-adjusted payments from CMS. In a previous CMS audit of high-risk diagnoses, 183 of the 280 sampled enrollee-years, resulted in the following findings: 1) the medical record(s) provided did not support the diagnosis code(s) or 2) the medical record(s) could not be located; therefore, the diagnosis code(s) was not validated. [3]
Through data mining techniques and meetings with medical professionals, CMS identified diagnoses that are at a higher risk of being miscoded. These diagnoses include:
- Major depressive disorder: Concerns related to this diagnosis note that the diagnosis was documented but the patient did not have an antidepressant medication prescribed. As such, a major depressive disorder may not be supported in the documentation.
- Acute stroke: Findings for this diagnosis noted that an acute stroke diagnosis on a physician claim during a service year does not correspond to an inpatient or outpatient hospital claim.
- Vascular claudication: The vascular claudication findings noted a diagnosis during the service year which was not present during the preceding 2 years.
- Cancer: Findings related to several cancer diagnoses in this audit was related to a cancer diagnosis during the service year, however no treatment (e.g., surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy) was found within a 6-month period before or after the diagnosis. A diagnosis of history of cancer may be more appropriate. These cancer diagnoses include:
- Breast cancer
- Colon cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Lung cancer
- Acute myocardial infarction (AMI): These specific findings noted diagnoses of acute myocardial infarction on a physician or outpatient claim during the service year. However, there was not an AMI diagnosis on a corresponding hospital claim. A code for the history of MI may be more appropriate.
- Embolism: Enrollees received a diagnosis of acute or chronic embolism without an anticoagulant medication, which is typically used to treat an embolism. The history of embolism diagnosis may be more appropriate.
These findings confirm the CMS intention to continue auditing for and enforcing complete and accurate clinical documentation.
UASI Suggested Compliance Activities for this Imitative
- Improve population health data analytical capabilities and monitor high risk diagnosis reporting.
- Utilize reports to determine the frequency of these high-risk diagnoses associated with risk-adjustment enrollees.
Minimally-Invasive Surgical (MIS) Fusion of the Sacroiliac Joint, June 2023
Documentation will be reviewed to determine whether minimally invasive surgical fusion of the sacroiliac joint met Medicare coverage criteria and was reasonable and necessary. The only code included in this review is CPT code 27279, Arthrodesis, sacroiliac joint, percutaneous or minimally invasive (indirect visualization), with image guidance, includes obtaining bone graft when performed, and placement of transfixing device. Additional procedure coding information can be found in the CPT Assistant, April 2023, Volume 33, Issue 4, page 16.
There are multiple different ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes that support the medical necessity for this procedure.
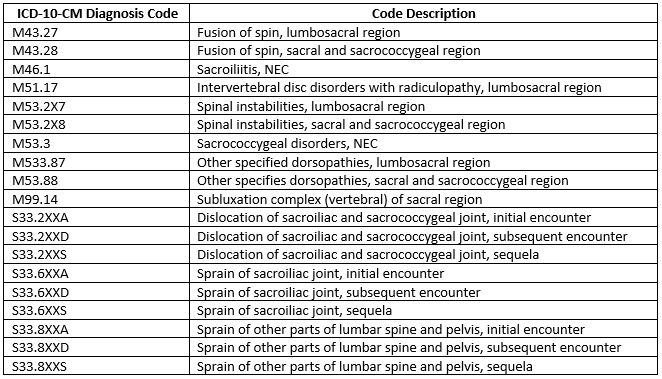
Coverage Indicators [4]
This procedure is considered medically necessary with ALL of the following criteria are met:
- Have moderate to severe pain with functional impairment and pain persists despite a minimum six months of intensive nonoperative treatment that must include medication optimization, activity modification, bracing, and active therapeutic exercise targeted at the lumbar spine, pelvis, SIJ, and hip including a home exercise program
- Patient’s report of typically unilateral pain that is caudal to the lumbar spine (L5 vertebrae), localized over the posterior SIIJ, and consistent with SIJ pain
- A thorough physical examination demonstrating localized tenderness with palpation over the sacral sulcus in the absence of tenderness of similar severity elsewhere and that other obvious sources for their pain do not exist
- Positive response to a cluster of 3 provocative tests
- Absence of generalized pain behavior
- Diagnostic imaging studies that include ALL of the following
- Imaging (plain radiographs and a CT or MRI) of the SI joint that excludes the presence of destructive lesions, fracture, traumatic SIJ instability, or inflammatory arthropathy that would not be properly addressed by percutaneous SIJ fusion.
- Imaging of the pelvis (AP plain radiography
UASI Suggested Compliance Activity for this Initiative
- Utilize reports to determine the frequency of CPT code 27279.
- Based on these findings, determine the need to audit a percentage of the total cases.
Transurethral Waterjet Ablation of the Prostate for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS), April 2023
Documentation will be reviewed to determine whether transurethral waterjet ablation services meet Medicare coverage criteria and were reasonable and necessary. CPT Category III code 0421T, Transurethral waterjet ablation of prostate, including control of post-operative bleeding, including ultrasound guidance, complete (vasectomy, meatotomy, cystourethroscopy, urethral calibration and/or dilation, and internal urethrotomy, are included when performed) and HCPCS code C2596, Probe, image-guided, robotic, waterjet ablation, are the two codes included in this RAC review.
This procedure is performed using water-jet hydrodissection (aqua ablation) to treat benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) of bladder outlet obstruction. Transrectal ultrasound imaging is used to map the target area and the surgeon programs a robotic system with precise tissue contours/depth. Using electromechanical control and real-time ultrasound guidance, a high-velocity stream of saline is delivered to the prostate via the urethra, which may require meatotomy, internal urethrotomy, and urethral calibration or dilation for access and successful ablation. The water jet selectively ablates the glandular tissue, which is simultaneously collected for post procedural laboratory analysis. A laser beam captured by a low-pressure water jet may be employed to obtain surface coagulation and hemostasis. Ultrasound guidance and control of post procedural bleeding are included as well as vasectomy and cystourethroscopy, when performed.
Coverage Indicators [5]:
Treatment for LUTS/BPH is considered reasonable and necessary when performed ONCE in patients with the following:
- Indications including ALL of the following:
- Age <80
- Prostate volume of 30-150 cc by transrectal ultrasound
- Persistent moderate to severe symptoms despite maximal medical management
Including ALL of the following
- International prostate symptom score >12
- Maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax) of <15 mL/s
- Failure, contraindication or intolerance to at least three months of conventional medical therapy for LUTS/BPH
- Only treatment using an FDA approved/cleared device will be considered reasonable and necessary
Limitations (the following are considered not reasonable and necessary):
- Body mass index >42
- Known or suspected prostate cancer, unless patient has had a negative prostate biopsy within the last 6 months
- Bladder cancer, neurogenic bladder calculus or clinically significant bladder diverticulum
- Active urinary tract or systemic infection
- Treatment for chronic prostatitis
- Diagnosis of urethral stricture, meatal stenosis or bladder neck contracture
- Damaged external urinary sphincter
- Known allergy to device materials
- Inability to safely stop anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents preoperatively
UASI Suggested Compliance Activities for this Initiative
- Utilize reports to determine the frequency of codes 0421T and C2596 and also the frequency of diagnosis code N40.1 with an associated CPT code.
- Based on these findings, determine the need to audit a percentage of both types of cases.
Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation for Obstructive Sleep Apnea (June, 2022)
The hypoglossal nerve stimulator is an implanted medical device that reduces the occurrence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) by electrically stimulating the hypoglossal nerve, which causes tongue movement. The stimulation is timed with breathing to relieve upper airway obstruction. The following CPT codes are including in this audit:
- 64582 – Open implantation of hypoglossal nerve neurostimulator array, pulse generator and distal respiratory sensor electrode or electrode array
- 64583 – Revision or replacement of hypoglossal nerve neurostimulator array and distal respiratory sensor electrode or electrode array, including connection to existing pulse generator
- 64584 – Removal of hypoglossal neurostimulator array, pulse generator, and distal respiratory sensor electrode or electrode array
Use modifier -52, reduced services, for removal of one or two components of the hypoglossal nerve electrode array, pulse generator, or distal respiratory sensor. Additional information on the use of these CPT codes can be found in CPT Assistant, March, 2022, Volume 32, Issue 3, page 7.
There are two categories if ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes required to justify this procedure:
- Group 1: G47.33, Obstructive sleep apnea (adult) (pediatric)
- Group 2: Secondary diagnosis – 16 code choices for BMI
- Z68.1 – Z68.34, Body mass index (ranging from 19.9 – 34.9)
Coverage Indicators [6]:
This procedure is considered medically reasonable and necessary for the treatment of moderate to severe OSA when all of the following criteria are met:
- Beneficiary is 22 years of age or older, and
- Body mass index (BMI) is less than 35 mg/m2, and
- A polysomnography (PSG) is performed within 24 months of first consultation for HGNS implant, and
- Beneficiary has predominantly obstructive events (defined as central and mixed apneas less than 25% of the total AHI), and
- AHI is 15 to 65 events per hour, and
- Beneficiary has documentation that demonstrates CPAP failure (defined as AHI greater than 15 despite CPAP usage) or CPAP intolerance (defined as less than 4 hours per night, 5 nights per week or the CPAP has been returned) including shared decision making that the patient was intolerant of CPAP despite consultation with a sleep expert and
- Absence of complete concentric collapse at the soft palate level as seen on a drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE) procedure, and
- No other anatomical findings that would compromise performance of device (e.g., tonsil size 3 or 4 per standardized tonsillar hypertrophy grading scale).
Limitations:
The following are considered not reasonable and necessary and therefore will be denied for CMS coverage:
- Hypoglossal nerve neurostimulation is considered not medically reasonable and necessary for all diagnoses not in group 1 or 2 above.
- Non-FDA-approved hypoglossal nerve neurostimulation is considered not medically reasonable and necessary for the treatment of adult OSA due to insufficient evidence of being safe and effective.
- Hypoglossal nerve neurostimulation is considered not medically reasonable and necessary when any of the following contraindications are present:
- Beneficiaries with central and mixed apneas that make up more than one-quarter of the total AHI
- Beneficiaries with an implantable device could experience unintended interaction with the HGNS implant system
- BMI equal to or greater than 35
- Neuromuscular disease
- Hypoglossal-nerve palsy
- Severe restrictive or obstructive pulmonary disease
- Moderate-to-severe pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Severe valvular heart disease
- New York Heart Association class III or IV heart failure
- Recent myocardial infarction or severe cardiac arrhythmias (within the past 6 months)
- Persistent uncontrolled hypertension despite medication use
- An active, serious mental illness that reduces the ability to carry out Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) and would interfere with the patient’s ability to operate the HNS and report problems to the attending provider
- Coexisting nonrespiratory sleep disorders that would confound functional sleep assessment
- Beneficiaries who are, or who plan to become pregnant
- Beneficiaries, who require MRI with model 3028, can undergo MRI on the head and extremities if certain conditions and precautions are met
- Beneficiaries who are unable or do not have the necessary assistance to operate the sleep remote
- Beneficiaries with any condition or procedure that has compromised neurological control of the upper airway
- Drug Induced Sleep Endoscopy (DISE)
- Shared Decision Making (SDM) shall be documented in the patient’s record by the referring physician and the implanting physician
UASI Suggested Compliance Activities for this Initiative
- Utilize reports to determine the frequency of CPT codes 64582, 64583 & 64584.
- Based on these findings, determine the need to audit a percentage of these cases.

End Notes:
1. OIG Work Plan: https://oig.hhs.gov/reports-and-publications/workplan/index.asp
2. CMS, Approved RAC Topics, last revised 6/6/2023, accessed on July 31, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Monitoring-Programs/Medicare-FFS-Compliance-Programs/Recovery-Audit-Program/Approved-RAC-Topics
3. Medicare Advantage Compliance Audit of Specific Diagnosis Codes that MCS Advantage, Inc. (contract H5577) Submitted to CMS. Medicare Advantage Compliance Audit of Specific Diagnosis Codes That MCS Advantage, Inc. (Contract H5577) Submitted to CMS, A-02-20-01008 (hhs.gov)
4. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. National Coverage Determination for Minimally-Invasive Surgical (MIS) Fusion of the Sacroiliac (SI) Joint. LCD ID: L36494. Effective date 2/1/016, revision effective date 1/5/2023, accessed on July 31, 2023. LCD – Minimally-Invasive Surgical (MIS) Fusion of the Sacroiliac (SI) Joint (L36494) (cms.gov)
5. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. National Coverage Determination for Transurethral Waterjet Ablation of the Prostate. LCD ID: L38705. Effective date 12/27/2020, accessed on July 31, 2023. LCD – Transurethral Waterjet Ablation of the Prostate (L38705) (cms.gov)
6. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. National Coverage Determination for Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. LCD ID: L38528. Effective date 6/14/2020, revision effective date 4/28/2022, accessed on July 31, 2023. LCD – Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea (L38528) (cms.gov)