Below are a collection of coding tips developed to shed light on the toughest scenarios. We hope these tips clarify any coding questions you might have related to these complex situations.
Table of Contents:
Use the links in the table of contents to jump to any section.
ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS Tips
- Addition of April 1st Maintenance of the ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS Coding Systems
- Z51.5 - Exempt from POA Reporting List
- Aspiration Fluid Biopsy of the Pubic Symphysis Joint
- Underimmunization for COVID-19 Status
- Correctly Coding Cerebrovascular Disease
- New Code - R45.88
- Newborn Observation due to Maternal Marijuana Use
- Nuchal Cord
- Impella
- New Coding Clinic for 2nd Quarter 2022
- Hyperlipidemia vs. Hypercholesterolemia
- Meconium
Addition of April 1st Maintenance of the ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS Coding Systems
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid (CMS) announced in the fiscal year 2022 Hospital Prospective Payment System final rule published on August 2,2021 that it is adopting an April 1 implementation date for ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS code updates, in addition to the annual October 1 update, beginning with April 1, 2022. The April 1 implementation will use a phased-in approach, such that the number and nature of code updates will be fewer and less comprehensive as compared to the existing October 1 update. “The intent of this April 1 implementation date is to allow flexibility in the ICD-10-CM/PCS code update process. CMS believes that this additional April 1 implementation date for new codes would allow for earlier recognition of diagnoses, conditions, and illnesses as well as procedures, services, and treatments in the claims data. The agency also believes this earlier recognition would be beneficial for purposes of reporting data collection, tracking clinical outcomes, claims processing, surveillance, research, policy decisions, and data operability.“1
1. AHIMA Journal September 20,2021 Highlights of FY 2022 IPPS Final Rule
Z51.5 - Exempt from POA Reporting List
Effective October 1,2021 , code Z51.5 Encounter for palliative care, was added to the Exempt from POA Reporting List by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics.
To find a list of all diagnoses that are exempt from POA reporting go to the CMS.gov website, click here.
Effective April 1, 2022 the following diagnoses have been designated as POA Exempt.
Z28.310 Unvaccinated for COVID-19
Z28.311 Partially vaccinated for covid-19
Z28.39 Other underimmunization status
Aspiration Fluid Biopsy of the Pubic Symphysis Joint
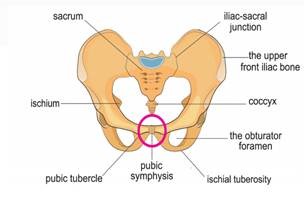
When an aspiration fluid biopsy of the pubic symphysis joint is performed a guide needle is passed percutaneously under CT guidance into the pubic symphysis joint. Serous fluid is obtained for analysis. Per Coding Clinic two codes are coded for this procedure in ICD-10-PCS.
0Q933ZX Drainage of left pelvic bone, percutaneous approach diagnostic, and
0Q923ZX Drainage of right pelvic bone, percutaneous approach, diagnostic, for aspiration biopsy of the pubic symphysis joint.
There is no specific body part value for drainage of the “pubic symphysis joint”. Thus, the body part values “3”, Pelvic bone, left, and “2”, Pelvic bone , right, would be appropriate to code for this procedure. “When the physician describes the pelvic symphysis as the body part, assign codes for both the left and right pelvic bones.”1
1. Coding Clinic for ICD10-CM/PCS, First Quarter 2022
Underimmunization for COVID-19 Status
Additional codes are assigned with category Z28.3 Underimmunization status codes, if applicable, to provide further information on reasons for underimmunization, such as contraindication (Z28.0-), patient’s decisions for reasons of belief or group pressure (Z28.1), patient’s decision for other and unspecified reason (Z28.2-), or other reason (Z28.8-).
“Codes in sub-subcategory Z28.31, Underimmunization for COVID-19 status, should not be assigned for individuals who are not eligible for the COVID-19 vaccines, as determined by the healthcare provider (e.g., infants too young to receive the COVID-19 vaccines).The ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting have been updated with instructions determining usage of codes Z28.310 and Z28.311 in relation to COVID-19 vaccinations.”1
1.AHA 2022 Number 1 First Quarter Coding Clinic Volume 9
Correctly Coding Cerebrovascular Disease
Gentle Reminder: Per AHA Coding Handbook it is appropriate to utilize reports to provide greater specificity of the anatomical site as documented by the provider. “Coding professionals may need to review an X-ray report to identify the location of a fracture, or an imaging report, such as a magnetic resonance (MRI) study, to determine the location of the infarction or stroke in a patient diagnosed with a cerebral infarction or hemorrhagic stroke.”
I60-I62 Non-Traumatic intracranial hemorrhage
I63 Cerebral Infarctions
I65-I66 Occlusion/stenosis of cerebral and precerebral vessels without infarction
I67-I68 Other cerebrovascular diseases
I69 Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease (late effect)
Code category I60-I62* specifies the location or source of a hemorrhage as well as its laterality.
Code category I63* specifies the following:
- Cause of the ischemic stroke
- Specific location and laterality of the occlusion
Code category I65-I66* requires the coder to be able to determine whether an occlusion or stenosis involves the precerebral arteries or the cerebral arteries.
- Precerebral arteries include:
- Vertebral artery
- Basilar Artery
- Carotid Artery
- Cerebral arteries include:
- Anterior cerebral artery
- Middle cerebral artery
- Posterior cerebral artery
Code category I67-I68* specifies other cerebrovascular diseases and cerebrovascular disorders in diseases classified elsewhere.
Code category I69* (Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease) specifies the type of stroke that caused the sequelae (late effect) as well as the residual condition itself. Codes from Category I69* also identify whether the dominant or non-dominant side is affected.
Coding guidelines state that the late effects (sequelae) caused by a stroke may be present from the onset of a stroke or arise at ANY time after the onset of the stroke.
If a patient is NOT EXPERIENCING A CURRENT CEREBROVASCULAR ACCIDENT (CVA) and has no residual or late effect from a previous CVA, Z86.73 (personal history of transient ischemic attack, and cerebral infarction without residual deficits) should be assigned. A patient experiencing no residual effects from a previous stroke should NEVER be assigned a current stroke code.
In order to accurately code sequelae (late effect) of cerebrovascular disease, the side of the body affected should be clearly documented in the medical record.
New Code Created - R45.88
The New code R45.88 has been created to describe non-suicidal self-harm. “The new code provides a way to differentiate between suicidal and non-suicidal self-harm, and allows non-suicidal self-harm to be treated and tracked in clinical databases.”1 In the past few years there has been an increase in non-suicidal self-harm also known as NSSI (non-suicidal self- injury). NSSI refers to the intentional destruction of one’s own body tissue without suicidal intent. Self-harm may include cutting, biting, burning, scratching, and banging or hitting.
“Self-harm is not a mental illness, but a behavior that indicates a need for better coping skills. It is a harmful way to cope with emotional pain, anger and frustration. Self- harm has less to do with the method used to hurt one’s body than the intention to hurt oneself.” 2
1,2 Coding Clinic for ICD-10-CM/PCS, Fourth Quarter 2021: Page 26
Newborn Observation due to Maternal Marijuana Use
The following question was asked in Coding Clinic First Quarter 2022.
How is the diagnosis of intrauterine drug exposure correctly reported on a newborn’s record? In the example given an infant was born via spontaneous vaginal delivery to a mom who had a history of marijuana use but stopped when she found out about her pregnancy. “There was no provider documentation indicating that the infant had any signs or symptoms of cannabis withdrawal; was affected by the maternal use of cannabis, nor any future healthcare implications for the baby.”
Because of the mom’s history, a urine drug screen was ordered for the infant. The results came back negative and the infant was discharged home.
Coding Clinic advised to code Z05.8 Observation and evaluation of newborn for other specified suspected condition ruled out, as a secondary diagnosis.
Codes from category Z05 are used for newborns within the neonatal period, who are suspected to have an abnormal condition, but without signs or symptoms, and which after examination and observation, is found not to exist.
Nuchal Cord
Nuchal cord is when the umbilical cord becomes wrapped around the fetus’s neck. A “Tight” nucal cord is defined as the inability to manually reduce the loop over the fetal head. This is not an uncommon condition as it occurs in 6.6% of over 200,000 consecutive live births in a multihospital health system.1 “A tight nuchal cord can cause obstruction of blood flow in the thin walled umbilical vein, while infants’s blood continues to be pumped out of the baby through the thicker walled umbilical arteries causing hypovolemia, acidosis and anemia.”2 Coding Clinic was asked what appropriate ICD-10-CM code should be assiged for a diagnosis of”tight nuchal cord” on a newborn record and if the diagnosis of tight nuchal cord indicated with compression or did the provider have to document with compression in order to assign code P02.5, Newborn affected by other compression of umbilical cord.
Per Coding Clinic “a tight nuchal cord does not necessarily imply compression. When coding the newborn’s record, the health record documentation should indicate the infant was affected in some way by the tight nuchal cord (e.g., metabolic accidosis, late decelerations, low Apgar score, etc). If the documentation is not clear whether the newborn was affected, query the provider for clarification.”3
1. Neonatal outcomes following a tight nuchal cord; Comparatie Study; J Perinatol.2013 Mar;33(3):231-4doi:10.1038/jp.2012.79
2. ACOG The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
3. First Quarter Coding Clinic 2022
Impella
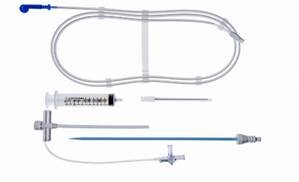
The intent of the Impella system therapy is to reduce ventricular work and to provide the circulatory support necessary to allow heart recovery and early assessment of residual myocardial function.
It is a minimally invasive, catheter-based external cardiac assist device. The pump is inserted percutaneously into the left ventricle (through a peripheral artery). The Impella device pumps blood for the left or right side of the heart into the ascending aorta or pulmonary artery. This is used to rest the patient’s heart during PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention) procedures and prevents the heart from being overstressed while the coronary artery blockages are repaired. The device maintains blood flow and blood pressure during the procedure. The device is also used in patients with advanced heart failure and has the ability to improve the quality of life for these patients when there are no other options available.
In 2017 the qualifier “intraoperative” was added to 02H for insertion of short term external heart assist system. Previously, guidance was to only code the assistance procedure (5A0) when the Impella was inserted during the surgery only and removed. However, with the addition of this qualifier, coders are now to report both 02HA3RJ Insertion of short-term external heart assist system into heart, intraoperative, percutaneous approach and a code from (5A0221D) that describes continuous assistance with cardiac output using an Impella pump.
If the Impella device is left in place for a few hours after surgery, the intraoperative qualifier would no longer apply since the device is still being utilized after patient has left the operating room. The ICD-10-PCS code for this situation would be reported as 02HA3RZ insertion of short-term external heart assist into heart, percutaneous approach and 5A0221D Assistance with cardiac output using Impeller pump, continuous.
A “Duration” of intermittent setting on the Impella® device has been added along with “continuous” so coders must look at the medical record to ascertain if the duration was intermittent or continuous.
The New Coding Clinic for Second Quarter 2022 has arrived!
Obesity
One of the coding questions asked in the new Coding Clinic pertains to coding obesity based on the documentation of the class of obesity. On the CDC website obesity is subdivided into categories.
Class 1: BMI of 30 to < 35
Class 2: BMI of 35 to < 40
Class 3: BMI of 40 or higher
The patient presented for follow-up for multiple medical conditions with Class 3 obesity being documented as one of those conditions. Coding Clinic confirmed that it would be appropriate to code E66.01 Morbid (severe) obesity for a Class 3 as it is synonymous with morbid obesity. But advised that a query would be necessary to determine the type or etiology of Class 1 and Class 2 if the documentation did not specify this information.
Hyperlipidemia vs Hypercholesterolemia
Many think that hypercholesterolemia and hyperlipidemia are synonymous but they are not. Hypercholesterolemia is the medical term for high blood cholesterol level. It is a waxy substance produced by the liver and a component of all cells found in the body. Hyperlipidemia is when you have to many lipids or fats in your blood. Hypercholesterolemia is a type of hyperlipidemia.
Causes of hyperlipidemia:
- Hereditary factors
- Diet rich in saturated fats and
- Cholesterol
- Some diseases
- Alcohol and smoking
- Some medications
Steroids
Coding clinic recommends coding E78.00, Pure hypercholesterolemia, unspecified, for a diagnosis of unspecified hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia. “Do not assign code E78.5, hyperlipidemia, unspecified, as the hypercholesterolemia identifies the specific blood lipid elevated.”1
Mixed hyperlipidemia means you have too much cholesterol and too much fat in your blood. Coding clinic recommends coding E78.2, Mixed hyperlipidemia, for a diagnosis of mixed hyperlipidemia with hypercholesterolemia and to not assign code E78.00, Pure hypercholesterolemia, unspecified, as the hypercholesterolemia is included in code E78.2.
1. AHA Second Quarter Coding Clinic 2022
Meconium
When a provider notes light meconium-stained fluid during delivery and the infant shows no sign of fetal distress, with Apgar score of 9 at one minute and 9 at five minutes assign ICD-10-CM diagnosis code O77.0, Labor and delivery complicated by meconium in amniotic fluid, for the light meconium staining since the presence of any meconium staining may indicate fetal stress.1
1.AHA Second Quarter Coding Clinic 2022
Monkeypox
The American Medical Association has announced new CPT codes designed to clinically distinguish the diagnostic test and vaccinations for monkeypox. They were created to support data-driven tracking, reporting and analysis necessary for resource planning and allocation during the public health response to the outbreak.
“The new laboratory test CPT code (87593) describes molecular diagnostic testing that detects the nucleic signature of an orthopoxvirus, including the monkeypox virus.”1
Laboratory test code – 87593 Infectious agent detection by nucleic acid (DNA or RNA): orthopoxvirus (eg, monkeypox virus, cowpox virus, vaccina virus), amplified probe technique, each
The two new vaccine codes are designed to describe the two smallpox and monkeypox virus products currently available.
90622 Vaccina (smallpox) virus vaccine, live, lyophilized, 0.3mL dosage, for percutaneous use
FDA-approved and manufactured by Sanofi Pasteur Biologics Co. for active immunization against smallpox disease for persons determined to be at high risk for smallpox infection.
90611 Smallpox and monkeypox vaccine, attenuated vaccinia virus, live, non-replicating, preservative free, 0.5 mL dosage, suspension, for subcutaneous use
FDA-approved JYNNEOS vaccine manufactured by Bavarian Nordic for prevention of smallpox and monkeypox disease in adults 18 years of age and older at high risk for smallpox or monkeypox infection.
1. AMA American Medical Association
Modifier 93
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been an increase in the use of telemedicine services, which are reported by appending modifier 95, Synchronous Telemedicine Service Rendered Via a Real-Time Interactive Audio and Video Telecommunications System, to the appropriate code(s).
“However, not all patients have access to the video piece of telemedicine technology. While there are specific codes within the CPT code set to report audio-only services, additional services may be provided via audio-only technology for which there is not a specific code. Rather than create all new codes to identify these services, modifier 93 was created to append to the appropriate code(s) to report these services. In addition, use of modifier 93 will allow for tracking of how often eligible services are performed using audio-only technology.”1
The descriptor for modifier 93 is as follows:
Modifier 93
Synchronous Telemedicine Service Rendered Via Telephone or Other Real-Time Interactive Audio-Only Telecommunications System: Synchronous telemedicine service is defined as a real-time interaction between a physician or other qualified health care professional and a patient who is located away at a distant site from the physician or other qualified health care professional. The totality of the communication of information exchanged between the physician or other qualified health care professional and the patient during the course of the synchronous telemedicine service must be of an amount and nature that is sufficient to meet the key components and/or requirements of the same service when rendered via a face-to-face interaction.
A speaker symbol has been added to the CPT code set to identify codes that are eligible to be reported with modifier 93.
1.CPT Assistant August 2022
Integumentary System
“Wound healing by primary intentions refers to healing wounds with edges that are approximated in a linear fashion by surgical suture, staples, and/or tissue adhesive. This type of healing may be accomplished with either a simple repair (12001-12021), intermediate layered closure (12031-12057), or complex layered closure (13100-13153).” Secondary intention is when a wound is left open (rather than being stitched together) and left to heal by itself, filling in and closing up naturally.
When a physician places autographs or skin substitutes onto the wound topically by use of steri-strips etc. to promote secondary intention healing report codes 15271-15278 for the topical application of skin substitute grafts.
Principles of CPT Coding, 9th Edition (p 144) state, “When a wound is left to heal by secondary intention (the spontaneous healing of a wound by granulation and new skin regrowth), it Is not appropriate to report codes 15002-15005 for the removal of nonviable tissue and/or debris from a chronic wound (eg, venous or diabetic). Instead, use the appropriate active wound management codes (97597, 97598) or debridement codes (11042 -11047) for this service. When necrotizing soft tissue infections in specific anatomic locations are treated, use codes 11004-11008.”
Pathology Clinical Consultation Services
Did you know?...Effective January 1st 2022 four new codes were created for pathology consult services per the CPT Assistant February 2022
The pathologist is provided with the patient's diagnosis and performs a review of the patient's history and medical records. The request for consultation may be made by a physician or other qualified health care professional and relates to path/lab test results, radiology findings, operative notes, or other clinical information that fall outside of an expected range or require additional medical interpretation. The consulting pathologist provides a written report of the findings at the conclusion. Codes are based on MDM and/or total time. Total time can include: Review of history, signs and symptoms; Arriving at a tentative conclusion; comparing against previous reports; ordering follow up testing; and counseling the clinician among others. Be sure to review the guidelines for these codes in your 2022 code-book.

Screening Colonoscopy
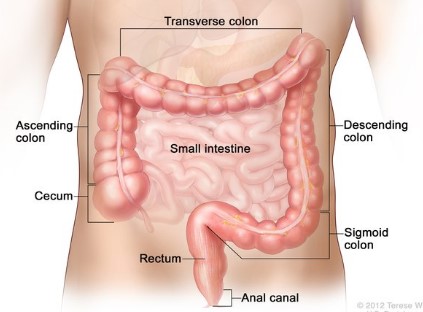
Colon Cancer is a 100% preventable. It starts as a growth inside the colon called a polyp. There are little to no symptoms of polyps growing in your large intestine. The main way we find them is by doing a “screening” test. Medicare provides coverage for screening colonoscopies to patients aged 50 and older. Many commercial insurers are now covering screening colonoscopies for patients 45 and over.
If a provider starts a screening colonoscopy and removes a polyp or another issue is found and removed during the screening colonoscopy, it turns into a diagnostic service.
To code a colonoscopy for commercial and or Medicaid patients report CPT code 45378 Colonoscopy, flexible: diagnostic, including collection of specimen(s) by brushing or washing, when performed (separate procedure). Append modifier 33 preventive services to the procedure code to trigger the preventive benefits (no cost sharing) to the patient. If the screening turns into a diagnostic procedure append modifier PT for a colorectal cancer screening converted to diagnostic test or other procedure.
When coding a screening for a Medicare patient report HCPCS Level II code G0105 Colorectal cancer screening; colonoscopy on individual at high risk or G0121 Colorectal cancer screening; colonoscopy on individual not meeting criteria for high risk.
Modifier 33 is not to be applied to these codes as screening is already indicated in the code descriptions.
Some indications a Medicare patient is at high risk for colorectal cancer are personal history or familial history (sibling, parent, or child) of adenomatous polyps, colorectal cancer, or inflammatory disease.
Per ICD-10-CM guidelines , “A screening code may be a first-listed code if the reason for the visit is specifically for the screening exam.” That code is Z12.11 Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of colon.
When anesthesia is used during a screening colonoscopy it may be reported separately with CPT code 00812. When a screening colonosocopy turns into a diagnostic colonoscopy, report the anesthesia service with CPT code 00811 and append modifier PT.

**Note moderate sedation is reported with HCPCS level II code G0500 or, if warranted CPT code99152-33 and 99153-33 based on time.
1. AAPC Healthcare Business Monthly, March 2022
Coding for Podiatry
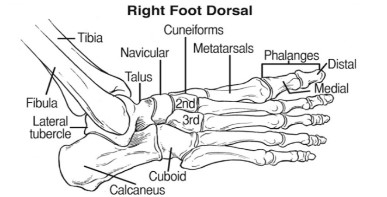
Podiatric medicine is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, and medical and surgical treatment of disorders of the foot , ankle, and lower extremity. Each foot contains 28 bones to include three main parts: tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges. Most of the common feet-related procedures are located in the code series (28001- 28899) of the CPT Manual. The tarsals are the seven bones that form the ankle. The metatarsals are the five bones that are located between the ankle and the toes. The phalanges are the 14 bones that form the toes.
Common podiatry procedures and codes
Hallux valgus corrections (28292- 28299)
Hallux valgus corrections are also known as bunionectomies of the great toe. The CPT codes for this procedure are located within the (28292-28299) series. A bunion is a medial protrusion of the distal end of the first metatarsal and lateral deviation of the great toe. Correction procedures vary in method and may include osteotomies or the insertion of implants, screws, or wire. “To select the correct code, coders must look closely at which bones are being altered and Identify where the physician is making the incision and where the screws are being placed.”1
CPT Code 28295 correction of hallux valgus with sesamoidectomy with proximal metatarsal osteotomy and CPT code 28298 correction of valgus hallux with sesamoidectomy with proximal phalanx osteotomy both describe bunionectomies that include osteotomy; however, CPT 28295 is reported for procedures that include the proximal metatarsal while CPT code 28298 is coded for those that include the proximal phalanx.
Eponyms for hallux valgus correction procedures include Akin osteotomy which is described by CPT code 28292 (correction, hallux valgus, with sesamoidectomy, when performed; with resection of proximal phalanx base, when performed, any method). “The scarf and chevron are two other terms for bunionectomy procedures whose descriptions fall under CPT code 28296 (correction, hallux valgus, with sesamoidectomy, when performed; with distal metatarsal osteotomy, any method).”2
Tailor’s bunion is a deformity of the fifth toe. A partial excision of the fifth metatarsal (28110) is typically performed to correct this deformity. When this procedure is performed alongside a bunionectomy, modifier 59 or XS is applied as it requires an additional incision on a separate anatomical structure.
Other podiatric diagnoses and procedures
Hammertoe is an abnormal bend of the middle phalangeal joint of the toe. Hammertoe correction procedures include interphalangeal fusion, partial or total phalangectomy. (see CPT code 28285).
Cock-up fifth toe is when the MTP joint of the smallest toe is dislocated or subluxated. The correction is reported with CPT code 28286, an incision is made under the fifth toe and the soft tissues are reflected to expose the proximal phalanx which is then removed leaving a space between the base of the metatarsal and the distal phalanx. The deep tissues and skin incisions are closed with sutures.
Arthrodesis is performed to prevent the mobility of bones and to stabilize hyperflexible or weak joints. CPT codes 28705-28760 are reported depending on the number of bones involved and/or if tendons are lengthened or metatarsals are fused to phalanges.
Do not forget to apply modifiers to identify which foot right (Rt) or left (Lt) for foot procedures and modifiers TA and T1 through T9 to identify procedures on toe digits.
1, 2 Savannah Schmidt, Clarify CPT coding for podiatric repair and reconstruction procedures, Just Coding May 4, 2022
Percutaneous Trigger Finger Release
In January’s 2022 CPT Assistant the question was asked “Is it appropriate to report code 26055 for percutaneous trigger finger release?”
The answer was no, a percutaneous trigger finger release does not require a tendon sheath incision. The recommendation is to report code 26989, Unlisted procedure, hands or fingers for the procedure.
In order to lessen the chance of payment denial for elective cases using this code, it is best to obtain prior authorization in writing from the payor before performing the procedure.
When prior authorization for an unlisted procedure is not obtained, a copy of the operative report should be submitted with supporting information outlining the decision-making process and the medical rationale for performing this procedure. Make sure you check with payors for their specific process as it may differ.
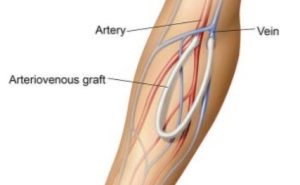
Coding for Arteriovenous Fistulas
Documentation Key Elements
- Anatomical location – Upper arm, antecubital, forearm or wrist
- What vessels are involved
- Number of incisions to accomplish the procedure
- Is there tunneling performed
- Are the vessels directly connected
- Is there grafting material used, if so, autogenous or synthetic
- If revision is performed, what is the status of the fistula – thrombosed or occluded or too deep to access
36818: Arteriovenous anastomosis, open; upper arm cephalic vein transposition. Medial side of the upper arm dissection & mobilize to cephalic vein; tunnel created on the anterior side of arm to transpose cephalic vein through bringing it the brachial artery for anastomosis
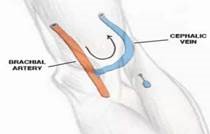
36819: Arteriovenous anastomosis, open; upper arm transposition. Medial side of the upper arm dissection & mobilize to basilic vein; tunnel created on the anterior side of arm to transpose basilic vein through bring it the brachial artery for anastomosis.
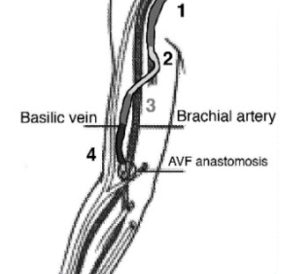
36821: Arteriovenous anastomosis, open; direct, any site. Artery and vein sites are identified and isolation of each vessel, dissecting the vein, and connecting in an end-to-side fashion. In some cases large venous branches may be tied off.
Only one incision is required, no transposition of vein and no tunneling necessary.
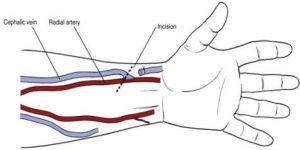
36825: Creation of arteriovenous fistula by other than direct arteriovenous anastomosis; autogenous graft. A harvested vein from the patient is used as the autogenous graft to create the anastomosis between the artery and vein by way of subcutaneous tunnel.
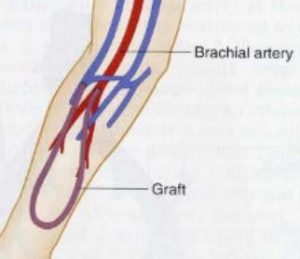
36830: Creation of arteriovenous fistula by other than direct arteriovenous anastomosis; nonautogenous graft (biological collagen, thermoplastic graft). Similar technique as 36825 with the exception of utilizing non-autogenous or synthetic graft material rather than the patient’s own vessel.